Management of Neonatal Hypoglycemia
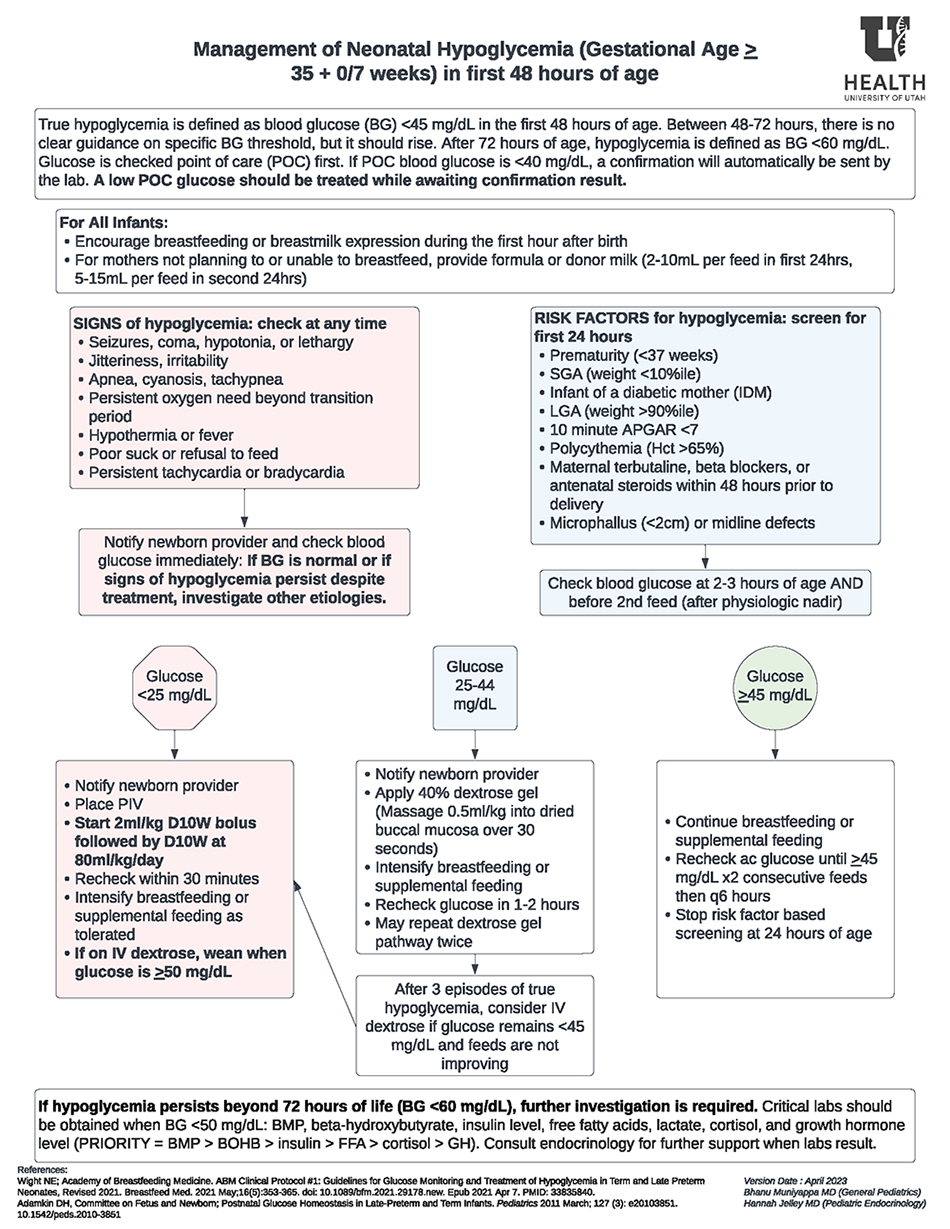
This 2023 care process model explains current practices for screening, testing, and treating hypoglycemia in newborns with gestational ages ≥35 0/7 in the University of Utah Hospital’s Well Baby and Intermediate Care Nurseries in the first 48 hours of life. Brief management recommendations for persistent hypoglycemia after 72 hours are also included.
Key Points
- Hypoglycemia is defined as a glucose < 45 mg/dL during the first 48 hours of age.
- Initiate breastfeeding within the first hour after delivery whenever possible. Use recommended volumes for formula or donor milk if breastfeeding is not an option.
- Check the first screening
glucose for infants with risk factors for hypoglycemia at 2-3 hours of life,
including:
- Prematurity (<37 weeks)
- Small for Gestational Age (SGA) (weight <10%ile)
- Infant of a diabetic mother (IDM)
- Large for Gestational Age (LGA) (weight >90%ile)
- 10-minute APGAR <7
- Polycythemia (Hematocrit >65%)
- Maternal terbutaline, beta-blockers, or antenatal steroids within 48 hours prior to delivery
- Microphallus (<2cm) or midline defects
- Check glucose immediately if
there are signs or symptoms of hypoglycemia, including:
- Seizures, coma, hypotonia, or lethargy
- Jitteriness, irritability
- Apnea, cyanosis, tachypnea
- Persistent oxygen need beyond transition period
- Hypothermia or fever
- Poor suck or refusal to feed
- Persistent tachycardia or bradycardia
- Treat low point of care (POC) glucoses while awaiting results with oral dextrose gel or intravenous (IV) dextrose, following the algorithm. POC glucoses <40 mg/dL will be sent automatically to the lab for confirmatory testing (this is a lab process based on error range of POC glucose). Don’t send confirmatory testing on POC glucoses >40 mg/dL.
- Use clinical judgment and nursing communication orders on how to wean dextrose infusion for glucoses >50mg/dL.
Management of Neonatal Hypoglycemia Care Process Map
Practice Guidelines
Wight NE.
ABM Clinical Protocol #1: Guidelines for Glucose Monitoring and Treatment of Hypoglycemia in Term and Late Preterm Neonates,
Revised 2021.
Breastfeed Med.
2021;16(5):353-365.
PubMed abstract
Adamkin DH.
Postnatal glucose homeostasis in late-preterm and term infants.
Pediatrics.
2011;127(3):575-9.
PubMed abstract
Patient Education
Resources
Information & Support
Related Portal Content Helpful Articles-
Abramowski A, Ward R, Hamdan AH.
Neonatal Hypoglycemia.
StatPearls. 2023. PubMed abstract
Authors & Reviewers
Page Bibliography
Abramowski A, Ward R, Hamdan AH.
Neonatal Hypoglycemia.
StatPearls.
2023.
PubMed abstract
Adamkin DH.
Postnatal glucose homeostasis in late-preterm and term infants.
Pediatrics.
2011;127(3):575-9.
PubMed abstract
Wight NE.
ABM Clinical Protocol #1: Guidelines for Glucose Monitoring and Treatment of Hypoglycemia in Term and Late Preterm Neonates,
Revised 2021.
Breastfeed Med.
2021;16(5):353-365.
PubMed abstract


 Get Help in Rhode Island
Get Help in Rhode Island