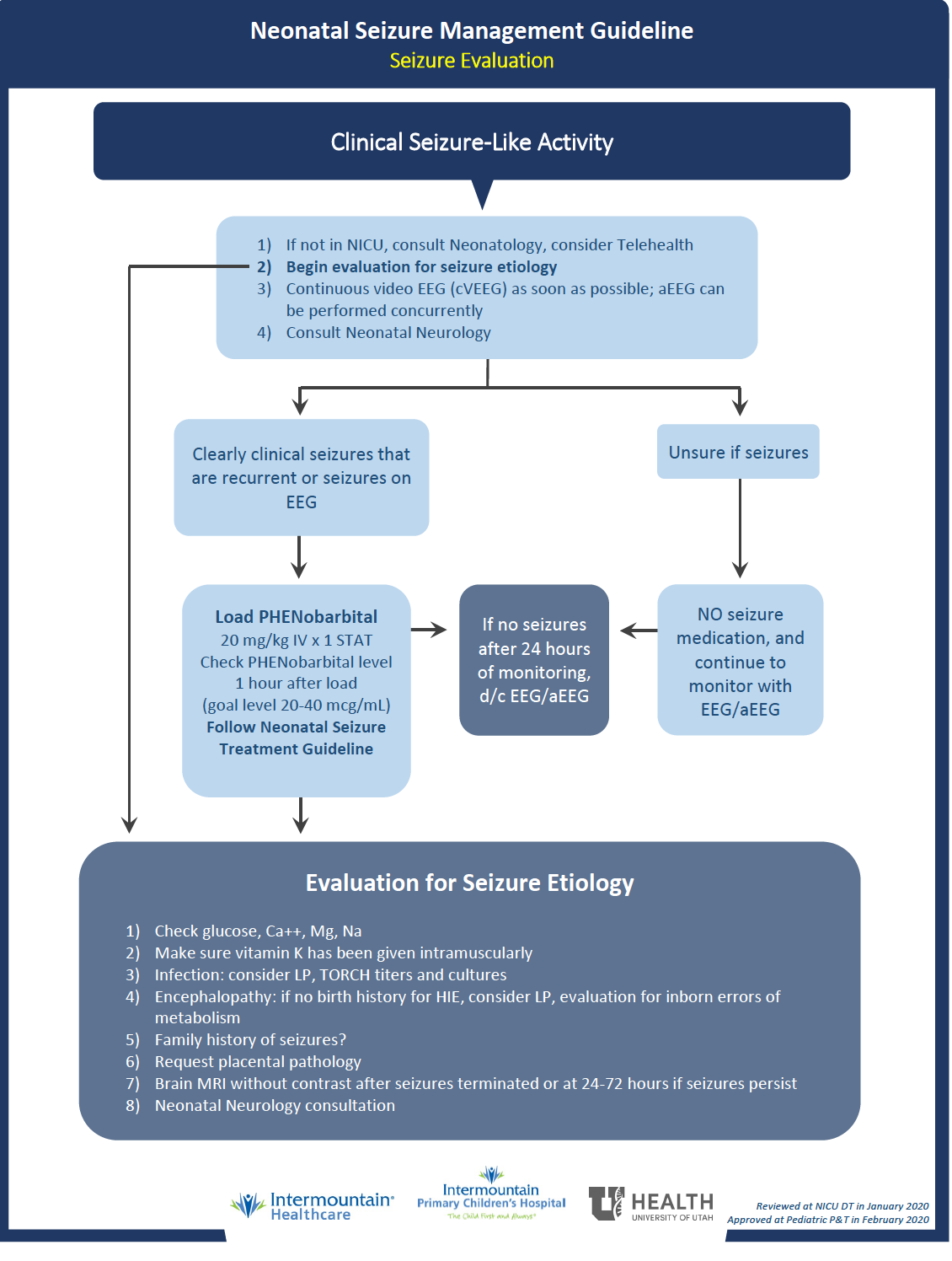
Suspected Neonatal Seizures Care Guidelines
Key Points
SymptomaticSeizures in newborns are often symptomatic seizures stemming from a brain injury, electrolyte abnormalities, or infection, not primary epilepsy.
In neonates, seizures tend to be focal rather than generalized.
When to consult neurology
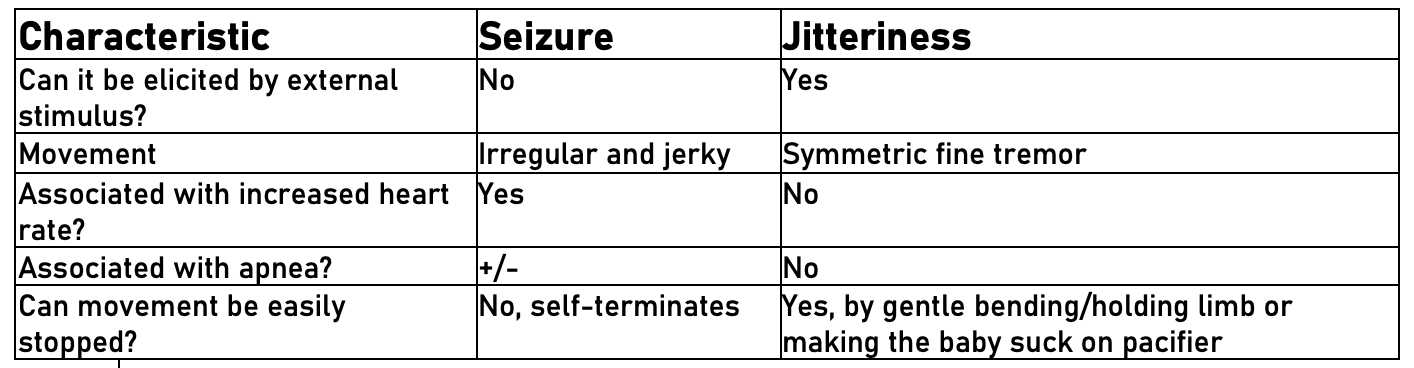
Use the Seizure versus Jitteriness Comparison Table (below)
and consider the clinical context to determine the likelihood of a neonatal
seizure, but when in doubt, urgently consult the Pediatric Neurology team
and transfer the infant to the NICU for an EEG.
Treat promptly
Promptly initiate treatment with phenobarbital or other
medications if there is strong clinical suspicion of seizures or as soon as
seizures are confirmed on EEG. See Management & Treatment below for
details.
Suspected Neonatal Seizures Care Guidelines
Cause of Neonatal Seizures
Seizures in a neonate are usually a symptom of brain injury rather than primary epilepsy. Eighty percent of neonatal seizures are caused by one or more of the following:- Stroke
- Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
- Infection
- Electrolyte abnormalities: hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia
Clinical Presentation
Diagnosis
Management and Treatment
- First-line treatment in neonates:
- Phenobarbital 20mg/kg IV x 1 dose STAT, can give additional 10mg/kg x 1 if seizure persists. Monitor for respiratory depression. Check PHB level prior to starting maintenance.
- Second-line treatment:
-
- Ativan 0.1mg/kg IV x 1 dose (has a very long half-life in neonates, between 24-40 hours)
- Fosphenytoin 20mg/kg IV x 1 dose
-
Neonatal Seizure Management Guideline
Referral & Services
Pediatric Neurology (see RI providers [18])Patient Education
Neonatal Seizures (UCSF)Resources
Information & Support
Related Portal Content
For Professionals
Critical Congenital Heart Screening (UDOH)
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease (CCHD) by pulse oximetry is mandatory for all Utah newborns effective October
1, 2014. This page has contact information for the Utah CCHD Screening Program and a link to screening results reporting form;
Utah Department of Health.
Information & Support
For Professionals
Neonatal Seizure (StatPearls)
This article reviews the evaluation and treatment of neonatal seizures and highlights the role of the interprofessional team
in evaluating and treating patients with this condition. CME available.
Services for Patients & Families in Rhode Island (RI)
| Service Categories | # of providers* in: | RI | NW | Other states (3) (show) | | NM | NV | UT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric Neurology | 18 | 5 | 5 | 8 | ||||
For services not listed above, browse our Services categories or search our database.
* number of provider listings may vary by how states categorize services, whether providers are listed by organization or individual, how services are organized in the state, and other factors; Nationwide (NW) providers are generally limited to web-based services, provider locator services, and organizations that serve children from across the nation.
Authors & Reviewers
| Author: | Betsy Ostrander, MD |
| Contributing Author: | Jennifer Goldman, MD, MRP, FAAP |


 Get Help in Rhode Island
Get Help in Rhode Island